Concrete Floor U Value

Related Images about Concrete Floor U Value
Lightweight Concrete Floor Systems – Thickness, Uses

Remember concrete flooring is usually covered with several materials like epoxy, an attractive sturdy finish which might be used just about anywhere in the home. Concrete office flooring is a green colored option that frequently outlasts other floor kinds as carpet, tile, wood, and linoleum.
High Quality Concrete Floor Installation S.A.M. Technologies

Yet another excellent trait of places which have polished concrete floors is that there is a high feeling of hygiene amongst the folks there. Concrete can be a great decision for flooring although it most likely isn’t for everyone. However there are additionally various other kinds of concrete that happen to be far more chic and stylish.
Concrete Sub-floor prep for ufh – Floor Structures – BuildHub.org.uk

Just before investing in some covering to your concrete floor, it have to be clean and free of any debris that could protect against bonding, including soil, oil or sealer. The flooring can complement the kitchen, creating a stunning masterpiece. No trees are actually cut down when concrete is actually made, a reduced amount of energy is actually manufactured to produce it as opposed to various other flooring sorts, and concrete flooring doesn’t contain volatile organic compounds.
Solid Concrete Floor – General Construction Issues – BuildHub.org.uk

Technical Info – Evolved Supplies

Pin on lower level
Grade-Supported Concrete Floors Cupolex

Soft concrete,FLOOR PREPARATION

Insulated Crawl Space. Concrete Block with 1-1/2 in. Interior Rigid Foam – GreenBuildingAdvisor

Prep + Level Concrete Floors Madness & Method

ALLIED CONCRETE PRODUCTS, INC. STRENGTH FOR LIFETIME USE

National Precast Concrete Association Australia Beams
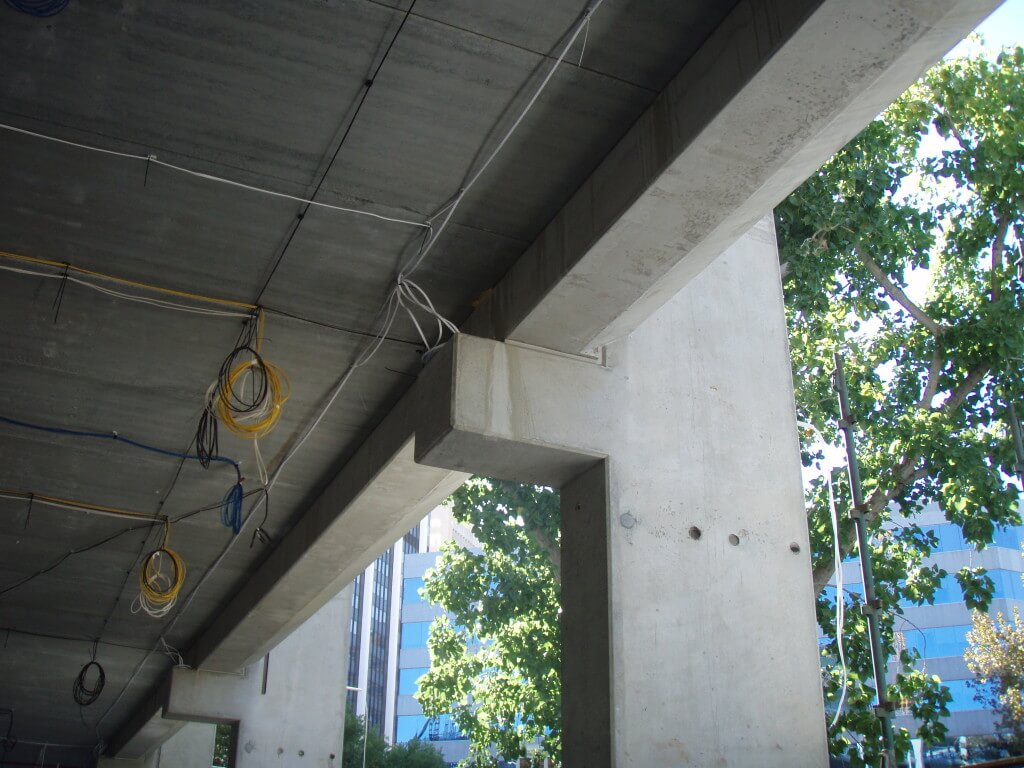

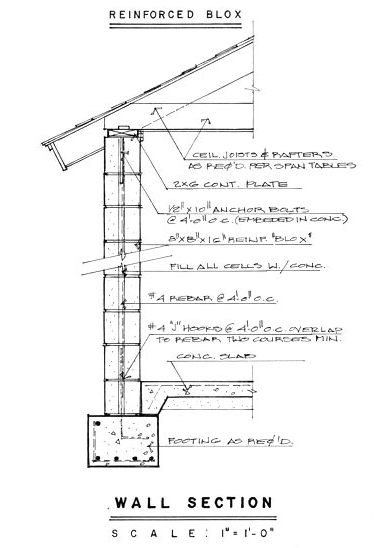
Greenstar Blox — A New Energy Efficient Wall Block
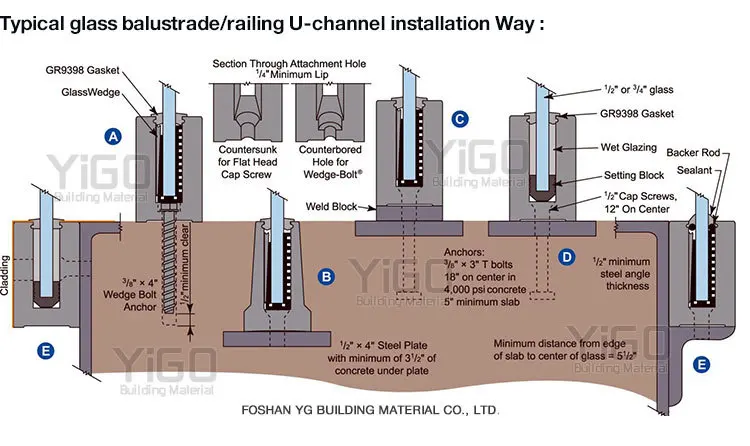
High Grade Stainless Steel Balustrade / Frameless U Channel Glass Balustrade – Buy Balustrade
Related Posts:
- Interior Concrete Floor Paint Ideas
- Concrete Floors In Homes Cost
- Level Concrete Floor With Plywood
- Concrete Floor Construction For Underfloor Heating
- Stained Concrete Floors In Basement
- Polished Concrete Floor Crack Repair
- Concrete Floor With Insulation
- Acid Stained Concrete Floors Pictures
- Installing Underfloor Heating On Existing Concrete Floor
- How Much Is Concrete Flooring
Concrete Floor U Value: An In-Depth Guide to Understanding and Optimizing Thermal Performance
Introduction:
When it comes to constructing energy-efficient buildings, understanding the thermal performance of different building components is crucial. One such component is the concrete floor, which plays a vital role in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and reducing energy consumption. In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of concrete floor U value, exploring its significance, factors affecting it, methods of calculation, and ways to optimize its thermal efficiency.
1. What is U value?
The U value, also known as the overall heat transfer coefficient, measures the rate at which heat is transmitted through a material or assembly. It represents the amount of heat that passes through one square meter of a component for every degree Celsius difference in temperature between its surfaces. The lower the U value, the better a material or assembly insulates against heat transfer.
2. Importance of Concrete Floor U value:
The U value of a concrete floor directly influences its thermal performance and energy efficiency. A low U value indicates that less heat is lost or gained through the floor, resulting in reduced energy consumption for heating or cooling purposes. By understanding and optimizing the U value of concrete floors, building owners can create comfortable living or working spaces while minimizing their carbon footprint and operating costs.
3. Factors affecting Concrete Floor U value:
Several factors contribute to the U value of a concrete floor, including:
a) Composition: The materials used in the concrete mix and their thermal properties significantly affect the overall U value. For instance, using lightweight aggregates or incorporating insulation materials within the concrete can improve thermal efficiency.
b) Thickness: The thickness of a concrete floor directly impacts its U value. Thicker floors generally have lower U values due to increased insulation properties.
c) Insulation: The presence of insulation beneath or within the concrete floor greatly influences its U value. Insulation materials such as expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene (XPS) can effectively reduce heat transfer.
d) Moisture content: Moisture within a concrete floor can affect its thermal conductivity and, subsequently, its U value. Proper moisture management during construction and the use of moisture-resistant materials are essential to maintain thermal efficiency.
4. Calculating Concrete Floor U value:
The U value of a concrete floor can be determined through a combination of theoretical calculations and experimental measurements. The most common method involves using specialized software or online calculators that take into account the various factors mentioned earlier. These calculators consider the dimensions, materials, insulation, and environmental conditions to provide an accurate U value estimation.
5. Optimizing Concrete Floor U value:
Achieving an optimal U value for a concrete floor requires careful planning and consideration of several factors. Here are some strategies to enhance its thermal performance:
a) Insulation: Adding insulation beneath or within the concrete floor is key to reducing heat transfer and improving its U value. High-quality insulation materials with low thermal conductivity should be selected based on the specific requirements of the building.
b) Vapor barriers: Installing vapor barriers between the subfloor and the concrete can prevent moisture from seeping into the floor, ensuring its long-term thermal efficiency.
c) Thermal breaks: Incorporating thermal breaks in the concrete floor construction can minimize heat loss through thermal bridging, where materials with higher conductivity create a path for heat transfer. Using insulating materials or spacing elements can help break these paths and improve overall thermal performance.
d) Finishes: Choosing appropriate finishes for The concrete floor can also contribute to its U value. Opting for finishes with higher thermal resistance, such as carpets or rugs, can provide additional insulation and improve overall thermal performance.
e) Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the concrete floor is crucial to ensure its long-term thermal efficiency. This includes addressing any cracks or gaps that may develop over time, as they can significantly impact the U value.
By considering these factors and implementing appropriate strategies, it is possible to optimize the U value of a concrete floor and enhance its thermal performance. The U value of a concrete floor refers to its overall thermal conductivity, or how well it conducts heat. A lower U value indicates better insulation and reduced heat transfer.
Insulation materials such as expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene (XPS) can effectively reduce heat transfer in a concrete floor, thus improving its U value.
Moisture content is another factor that can affect the U value of a concrete floor. Moisture within the floor can increase its thermal conductivity and reduce its insulation properties. Proper moisture management during construction, as well as the use of moisture-resistant materials, is essential to maintain thermal efficiency.
To calculate the U value of a concrete floor, a combination of theoretical calculations and experimental measurements is usually used. Specialized software or online calculators take into account factors such as dimensions, materials, insulation, and environmental conditions to provide an accurate estimation.
To optimize the U value of a concrete floor, several strategies can be employed. Adding insulation beneath or within the floor is key to reducing heat transfer and improving its U value. High-quality insulation materials with low thermal conductivity should be chosen based on specific requirements.
Installing vapor barriers between the subfloor and the concrete can prevent moisture from seeping into the floor, maintaining its long-term thermal efficiency.
Incorporating thermal breaks in the construction of the concrete floor can minimize heat loss through thermal bridging. Insulating materials or spacing elements can help break these paths and improve overall thermal performance.
Choosing finishes with higher thermal resistance, such as carpets or rugs, can provide additional insulation and improve the U value of the concrete floor.
Regular maintenance of the concrete floor is crucial to ensure its long-term thermal efficiency. Addressing any cracks or gaps that may develop over time is important as they can significantly impact the U value.
By considering these factors and implementing appropriate strategies, it is possible to optimize the U value of a concrete floor and enhance its thermal performance.
